What is the difference between A193 Grade B7 and A193 Grade B7M Studbolts? |
Different ASTM specifications are followed by an 'M' indicating that it is an equivalent metric standard. While there is actually an A193M Grade B7 specification that applies to metric fasteners, this is not the case with ASTM A193 Grade B7M. This is a different type of material than A193 Grade B7. So how exactly is A193 Grade B7M different from A193 Grade B7?
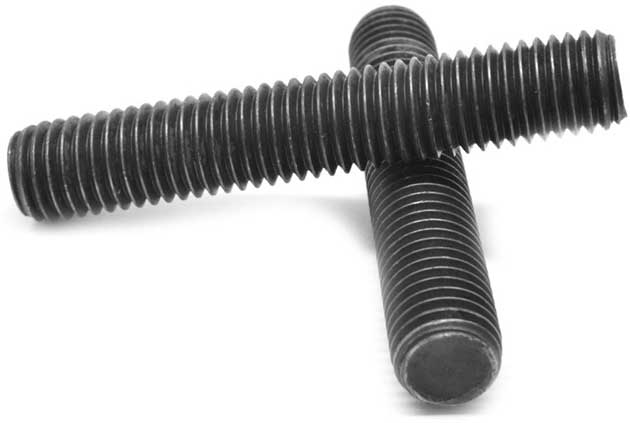

There are some significant differences in both the mechanical properties and testing requirements of A193 B7M and A193 B7. For example, A193 B7M has a minimum tensile strength of 100 ksi for diameters under 4in. The minimum tensile strength for A193 B7 is 125 ksi for diameters less than 2-1/2in, and 115 ksi for diameters 2-1/2in - 4in.
Hardness is probably the most important difference between A193 B7M & A193 B7. The maximum hardness of ASTM A193 B7M is 235 HB or 99 HRB, while the maximum hardness of A193 B7 is 321 HB or 35 HRC. The most notable difference from a manufacturing perspective is that when supplying A193 B7M bolts, each individual bolt or stud in the batch must be tested for hardness. A193 B7M fasteners also require a different type of heavy-duty hex nut than A193 B7, namely ASTM A194 Grade 2HM.
While A193 B7 is specified relatively often in the construction industry, A193 B7M is a specification not seen as regularly. This makes it important to understand the differences between the two specifications so that the right material is ultimately supplied.
Reference(s) .. www.portlandbolt.com
Mechanical properties B7
ASTM A193 Grade B7 bolts and studs are manufactured from a chromium-molybdenum steel and are quenched and tempered (heat treated) to develop the desired mechanical properties (strength). Grade B7 is the most commonly used grade of A193 bolts in construction. B7 threaded bolts and short head bolts are available on the market. Grade B7 bolts are often used in pipe flange connections. These bolts are usually purchased and sold in bare metal, but are often hot-dipped galvanized, zinc-plated, Xylan-coated, PTFE-coated or otherwise coated for corrosion resistance. Note that coated bolts may not withstand the high temperatures to which uncoated B7 bolts may be exposed.
| Grade | Size Inches | Tensile ksi, min | Yield, ksi, min | Elong, %, min | RA % min | HBW | HRC |
 |
Up to 2.1/2 | 125 | 105 | 16 | 50 | 321 max | 35 max |
| 2.5/8 to 4 |
115 | 95 | 16 | 50 | |||
| 4.1/8 to 7 |
100 | 75 | 18 | 50 |
Mechanical properties B7M
ASTM A193 Grade B7M bolts and studs are identical in chemical composition to Grade B7 (quenched and tempered medium carbon alloy steel), but have lower strength requirements and require 100% hardness testing of all fasteners manufactured in the batch. Grade B7M bolts are resistant to chloride, sulfide and hydrogen corrosion cracking (SCC) and are often used in the use of acid gases.
| Grade | Size Inches | Tensile ksi, min | Yield, ksi, min | Elong, %, min | RA % min | HBW | HRC |
 |
Up to 4 | 100 | 80 | 18 | 50 | 235 max | - |
| Over 4 - 7 |
100 | 75 | 18 | 50 |

Related Post(s)

Xylan coating is an extreme performance coating, explicitly designed to enhance performance and extend the service life of various industrial products...