Bolts and Nuts for flanged connections |
Types of Bolts
In Petro and chemical industry for flange connections Stud Bolts and Hex Bolts are used. The Stud Bolt is a threaded rod with 2 heavy hexagon nuts, while the Hex Bolt has a head with one nut. Nuts and head are both six sided.
Stud Bolts general
The quantity of bolts for a flange connection will be given by the number of bolt holes in a flange, diameter and length of bolts is dependent of flange type and Pressure Class of flange.
Stud Bolt length are defined in ASME B16.5 standard. The length in inches is equal to the effective thread length measured parallel to the axis, from the first to the first thread without the chamfers (points). First thread is defined as the intersection of the major diameter of the thread with the base of the point.
Studs are measured parallel to the axis (L) from
the first to the thread without the chamfers (points)
S = free threads equals 1/3 time bolt dia
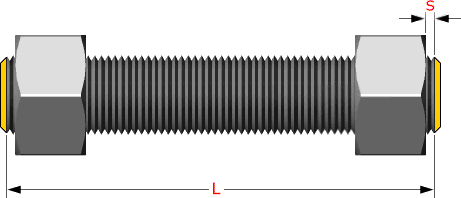
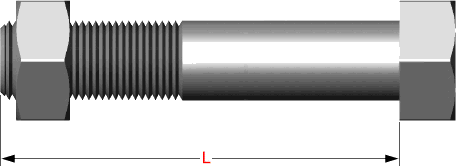
Hex bolts are measured from under the head to the end of the bolt
Note..
- To allow the use of hydraulic tensioning equipment, larger dimension studs shall be often one diameter longer than "standard". That bolts to have plastic end cap protection.
Threads of Stud Bolts
Bolts threading are defined in ASME B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads, (UN and UNR Thread Form).
The most common thread is a symmetrical form with a V-profile. The included angle is 60°. This
form is widely used in the Unified thread (UN, UNC, UNF, UNRC, UNRF) form as the ISO / metric threads.
The advantage of a symmetrical threads is that they are easier to produce and inspect compared with
non-symmetrical threads. These are typically used in general-purpose fasteners.
Thread series cover designations of diameter/pitch combinations that are measured by the number
of threads per inch (TPI) applied to a single diameter.
Standard Thread Pitches
- Coarse thread series (UNC/UNRC) is the most widely used thread system and applied in most of the screws, bolts and nuts. Coarse threads are used for threads in low strength materials such as iron, mild steel, copper and softer alloy, aluminium, etc.. The coarse thread is also more tolerant in adverse conditions and facilitate quick assembly.
- Fine thread series (UNF/UNRF) is commonly used in precision applications and in there where require a higher tensile strength than the coarse thread series.
- 8 - Thread series (8UN) is the specified thread forming method for several ASTM standards including A193 B7, A193 B8/B8M, and A320. This series is mostly used for diameters one inch and above.
Hex Nuts
Hex nuts (dimensional data) are defined in ASME B18.2.2, and even as bolts the threading in ASME B1.1. Depending on a customer specification, nuts must be both sites chamfered or with on one side a washer-face.
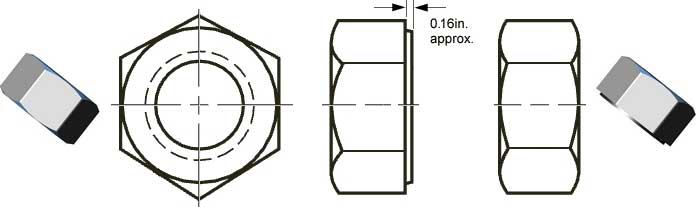
Dimensions of above mentioned nuts, can be found on page Heavy Hex Nuts of this website.
The height of a nut for a Stud Bolt is the same as the diameter of the thread rod
Materials for Stud Bolts
Dimensions from Stud Bolts are defined in the ASME B16.5 standard. The material qualities for studs are defined in the different ASTM standards, and are indicated by Grade. Frequently used grades are A193 for thread rods and A194 for the nuts.
ASTM A193 covers alloy and stainless steel bolting material for pressure vessels, Valves, flanges,
and fittings for high temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose applications.
ASTM A194 covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and martensitic and austenitic stainless steel nuts.
These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service, or both.
Marking of Stud Bolts
Thread rods and nuts must be marked by the manufacturer with a unique identifier to identify the manufacturer or private label distributor, as appropriate. Below a number of ASTM examples.
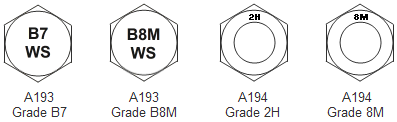
Grades of Stud Bolts
Below a table with materials and grades for flanges, thread rods (bolts) and nuts, arranged on design temperature, flanges, thread rods and recommended nuts.
| DESIGN TEMP. |
FLANGES | GRADE THREAD RODS |
GRADE NUTS |
| -195° to 102°C | ASTM A182 Gr. F304, F304L, F316, F316L, F321, F347 |
A320 Gr.B8 Class2 | A194 Gr.8A |
| -101° to -47°C | ASTM A350 Gr.LF3 |
A320 Gr.L7 | A194 Gr.7 |
| -46° to -30°C | ASTM A350 Gr.LF2 |
A320 Gr.L7 | A194 Gr.7 |
| -29° to 427°C | ASTM A105 | A193 Gr.B7 | A194 Gr.2H |
| 428° to 537°C | ASTM A182 Gr.F11, F22 |
A193 Gr.B16 | A194 Gr.2H |
| 538° to 648°C | ASTM A182 Gr.F11, F22 |
A193 Gr.B8 Class1 | A194 Gr.8A |
| 649° to 815°C | ASTM A182 Gr. F304H, F316H |
A193 Gr.B8 Class1 | A194 Gr.8A |
| DESIGN TEMP. |
FLG'S | GRADE THREAD RODS |
GRADE NUTS |
Note.. Materials in the table above are being provided for guidance purposes
Remark(s) of the Author...
Improper Flange Connections - the Bolts are too short!
What can you do..
- The picture show a improperly bolted flange, because two bolts are too short, and the nuts are not completely on the bolts. This means that the joint may not be as strong as it should be. Flanges are designed so that the entire nut-bolt combination holds the forces on the flange. If the nut is only partially screwed onto the bolt, the connection may not be strong enough.

- If your job includes putting equipment together, assembling flanged pipe, bolting manhole covers or other bolted connections on equipment, or other equipment assembly, remember that the job is not complete until all of the bolts are properly installed and tightened.
- Some equipment requires special bolt tightening procedures. For example, you may have to use a torque wrench to correctly tighten the bolts to the specification, or tighten the bolts in a special order. Make sure that you follow the correct procedure, use the correct tools, and that you are properly trained in the equipment assembly procedure.
- Check pipes and equipment for properly bolted flanges as part of your plant safety inspections. As simple guidance, bolts that do not extend beyond the nuts should be reviewed by a plant piping craftsman or engineer.
- If you observe improperly bolted flanges in your plant, report them so they can be repaired, and make sure the required repairs are completed.
- Inspect new equipment, or equipment which has been re-assembled after maintenance, to make sure it is correctly assembled and properly bolted before starting up.
What is the proper length of a Stud Bolt..
As a rule, you can use..
The free threads of the bolt above the top of the nut is equals to 1/3 times the bolt diameter.