|
What is cold forging? |
As a major metal fabrication, forging is a metal forming technique that uses localized forces of compression. Forgings have undergone major changes that lead to more efficient, faster and more durable processes. Today’s forging is usually done using electric, hydraulic or compressed air driven forging presses or hammer tools.
Cold forging, unlike hot forging, deforms metal below its recrystallization point - near or at room temperature. Cold forging is a preferred method for softer metals (such as aluminum), is less expensive and has the ability to produce forged parts that require little finishing.
A cold machining process, cold forging involves placing bar material in a die and then pressing it with a second closed die.
Similar to the cold press process (except that cold forging uses vertical presses instead of horizontal cold press machines), the workpiece is pressed between two dies until it assumes the desired shape of the die.
Deformation occurs at room temperature, changing the size and shape of the metal. This forging method is volume specific and generally complements cold pressing, adding more complex shapes to the blank used in cold pressing.
The basic equipment used for the forging method includes vertical presses, either fully automatic or manual. These vertical presses can be driven either hydraulically or mechanically.
A reliable and cost-effective process that includes producing parts for the electric car industry:
- Parts for car seats and alternators (such as the claw-pole).
- Different types of gears used on other parts.
- Parts for starter motors such as transmission solenoid body, core and plunger, to name but a few examples).
- Motorcycle parts such as those for flywheel magnetos.
- Parts that are hollow with shafts and stems.
- Parts used for valves and switches.
- Cold forging is also used to produce anti-vibration spiders and parts.
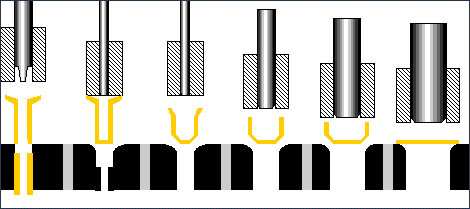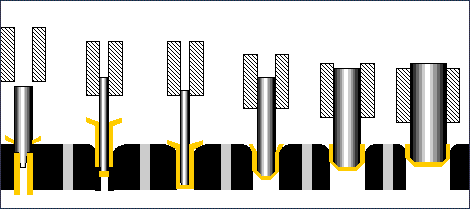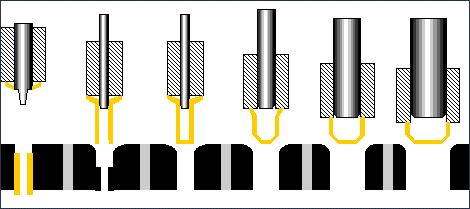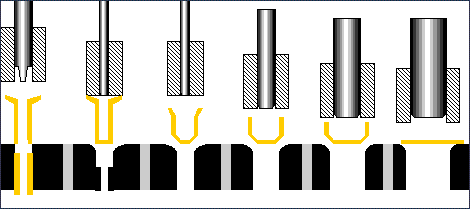 Image animation..www.ulbrich.com
Image animation..www.ulbrich.com
The benefits of cold forging
This particular forging process, offers manufacturers a number of advantages, including..
- Cold forging does not require heating.
- This forging process offers better interchangeability and reproducibility.
- Better surface finish is achieved and contamination problems are minimized.
- Cold forging offers superior dimensional control.
- The ability to assign targeted properties to the metal formed.
The disadvantages of cold forging
Cold forging has the following disadvantages..
- The production of an undesirable residual stress.
- The forged metals are less ductile and higher forces are required in cold forging.
- Because of the higher forces required in this process, heavier and more powerful equipment is needed, as well as stronger tools.
- Although the metal can acquire directional properties, these properties can be detrimental.
- The surfaces of the metals used must be clean and free of tarnish.
- Because of the loss of ductility associated with stress hardening, intermediate annealing may be necessary.
Cold Forging Animation