Thermite Welding |
Thermite welding, also called exothermic welding, is a specialized welding process in which metal components are joined using a chemical reaction instead of an external heat source.
Thermite welding is a fusion welding process in which a chemical reaction occurs between metal oxides and aluminum. This reaction generates enormous heat, which can reach temperatures of up to 2500°C (4532°F).

The Science Behind the Process
The thermite process was discovered in 1893 and patented in 1895 by the German chemist Hans Goldschmidt. The reaction is therefore also called the "Goldschmidt reaction" or "Goldschmidt process" and since the turn of the century the thermite process has been used for connecting train tracks and for other applications in the transportation sector.
The core of thermite welding is the thermite mixture, which consists of finely powdered metal oxides and aluminum. When ignited, the aluminum reduces the metal oxides, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat. This exothermic reaction is highly controlled and provides the heat needed to melt the metals being joined.
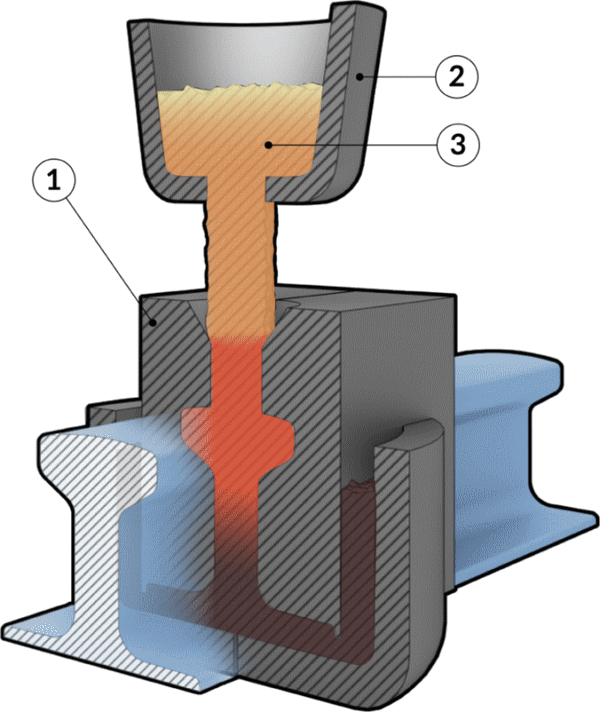
Process the workpieces to be joined are aligned with a suitable spacing. Each application requires a mold 1 specifically designed to fit the profile of the workpieces. The process is largely similar to a standard casting process.
After preheating, the combustion chamber is replaced with a container 2 containing thermite 3 When the thermite is ignited, so much heat is generated that it melts the thermite steel, which then flows into the gap between the profiles.
Once the melt has partially cooled, the mold is removed and post-processing, such as grinding, takes place to eliminate any irregularities and weld cracks. It is desirable that the weld profile fits perfectly against the workpieces.
Thermite welding applications
Railways: Joining of rails in tracks.
Construction: Welding pipelines, bridges, and structural components.
Shipbuilding: Connecting metal plates for ship hulls.
Automotive: Repairing heavy machinery and vehicles.
Ensuring Safety During Thermite Welding
Safety is paramount in thermite welding. Proper protective clothing, a controlled work environment, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to prevent accidents and injuries.
In addition, personal protective equipment such as heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses are crucial to ensure the safety of the welder and other employees.

Conclusion.. Thermite welding, with its ingenious use of chemical reactions to create strong metal bonds, has revolutionized several industries. The ability to create durable, reliable joints without the need for external power sources makes it a valuable welding technique. As the technology continues to develop, thermite welding is expected to further improve its precision, efficiency, and applications, contributing to a more sustainable and connected world.
Reference(s)..
www.manufacturingguide.com
freaktools.co
Related Post(s)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding is a welding method that is somewhat unique compared to Metal Inert Gas welding (MIG)...