Tips and Notes
Hydraulic bolt tensioning involves axially stretching the bolts using hydraulic pressure to achieve the desired preload and high integrity of the flange connections. Below are some guidelines on when and for which diameters bolt tensioning is necessary:
- For all flange connections with bolt diameters of 1.5 inches and larger.
- For all flange connections with pressure class 600 and higher.
- For all flange connections in hydrogen and toxic environments with bolt diameters of 1.5 inches and larger.
- For all flange connections exposed to high temperatures with bolt diameters of 1 inch and larger.
The guidelines are based on the experiences of various large companies in the oil and petrochemical industry and may vary from customer to customer.

Read more at.. Bolt Tensioning in more detail
In metal production, a heat refers to a specific, separate batch of material from a single furnace cycle, which determines its unique chemical composition, while a lot is a broader group of products (possibly from multiple heats) that have been processed, heat-treated, or produced under identical conditions for quality control and traceability purposes.
Spectacle blinds with a diameter greater than 24 inches are not covered by ASME B16.48.
Currently (January 2026), there are no reliable values known for these dimensions.
However, ASME B31.3 section 304.5.3 describes a formula that can be used to calculate these values.
The minimum required thickness of a permanent blank can be calculated using the following equation.
Where
- c = sum of allowances defined in section 304.1.1
- dg = inside diameter of gasket for raised or flat face flanges, or the gasket pitch diameter for ring joint and fully retained gasketed flanges
- E = same as defined in section 304.1.1
- P = design gage pressure
- S = same as defined in section 304.1.1
- W = same as defined in section 304.1.1
In order to perform the calculations, it is important (necessary) to have the ASME B31.3 standard (Process Piping) available.
When performing a hydrostatic test on ball valves and associated pipes, the manufacturer's recommendations must be followed. In general, the pipe system is filled with water while the ball valves are fully open. Before performing the test, it is advisable to flush the system to remove all dirt. During flushing, the valves are usually removed and replaced with flushing pieces to prevent damage to the valve seats from dirt and other construction debris.
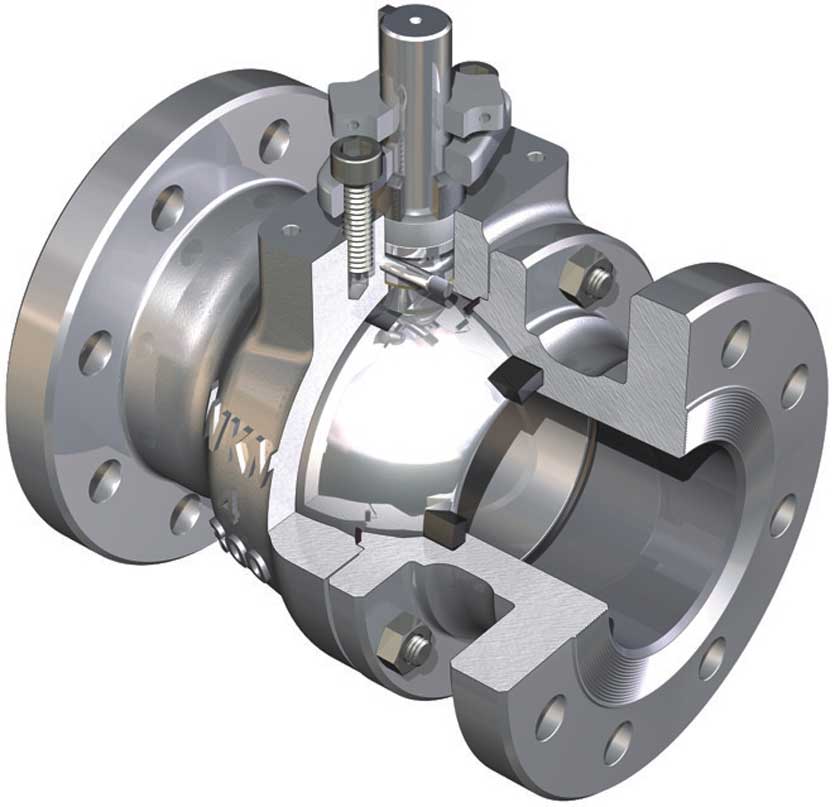
After the pipes have been flushed and filled with water, the ball valves are partially opened before the system is pressurized to prevent pressure differences between the valve housing space and the piping system. After the system has been fully pressurized, the valves are checked for leaks at the spindle seal and other screw connections. After the hydrostatic test, the valves must be fully opened again. The valves should not be left in the partially open position for long periods of time, as this can damage the elastomers in the seat ring and ultimately cause leakage.
API 598 - Hydrostatic test of Ball valve
On-Stream Inspection (OSI), uses irradiation testing to verify wall thickness, erosion or corrosion points based on digital image files or analog X-ray films.

Read more at.. What is On-stream inspection?
Pneumatic pressure testing of piping and vessels at moderate-to-high test pressures or at low test pressures with high volume is more hazardous than hydrostatic pressure testing because the stored energy is much greater with compressed gases or air.

Read more at.. What are Risks of Pneumatic pressure testing
The Flange Weld Tester is used to hydrotest the integrity of new welds where a Weld(ing) Neck or Slip On flange has been added to a pipeline.
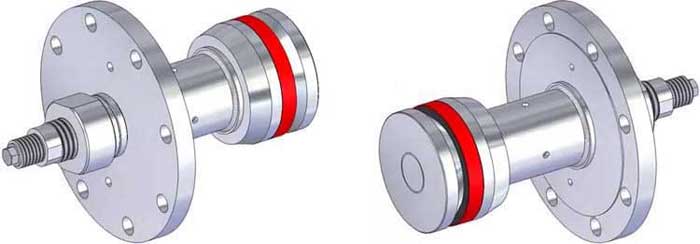
Read more at.. What are Flange Weld Testers?
Dip pipes have a wide range of applications. They are typically used to fill a reactor or storage tank below the liquid level, to extract samples from the equipment.
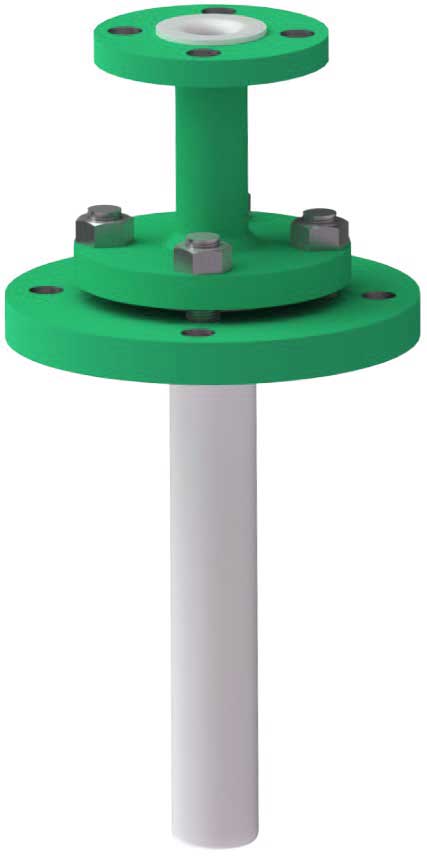

A dip pipe also serves as a component to drain liquid from a vessel without the need for a side or bottom outlet.
Read more at.. What are Dip Pipes?
Water hammer usually occurs after the pump has been switched off, but can also be caused by the rapid opening or closing of a valve.

This causes shock waves, also called pressure surges or water hammers, to move back and forth in the piping system at the specific speed of sound of the fluid in question.
Read more at.. What is Water Hammer?
Fireproofing, a passive fire protection measure, refers to the act of making materials or structures more resistant to fire, or to those materials themselves, or the act of applying such materials.
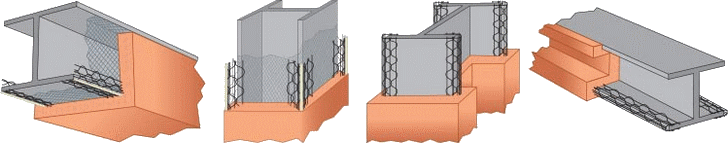
Read more at.. Is Fireproofing for Petrochemical facilities
Most people are not sure whether stainless steel is magnetic or non-magnetic. Some think it could be magnetic because it contains traces of iron, but in practice the answer is neither yes nor no.

Read more at.. Is Stainless Steel magnetic?
Under a unit rate contract, a construction company prices separate parts, or units, of the work to estimate the total project cost. Each unit is based on several variables, in combination or separately, such as materials, labor and overhead.

Read more at.. What is a Unit rate contract?
Unlike orthographics, piping isometrics allow the pipe to be drawn in a manner by which the length, width and depth are shown in a single view. Isometrics are usually drawn from information found on a plan and elevation views.
Read more at.. How to read a Piping Isometric?
Flange gaskets are used to create a static seal between two flanges faces, at various operating conditions, with varied pressure and temperature ratings.
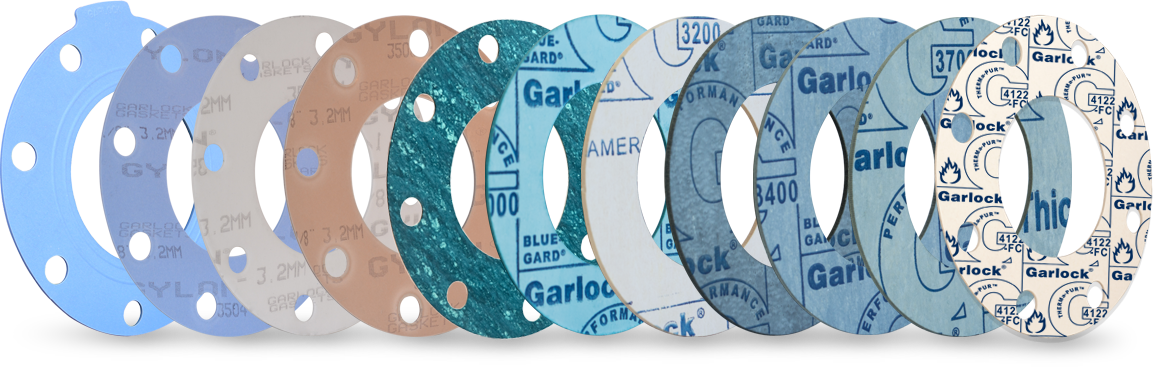
Read more at.. Gaskets for flanged Connections
Eddy current array (ECA) is a nondestructive testing technology that provides the ability to electronically drive multiple eddy current coils, which are placed side by side in the same probe assembly.
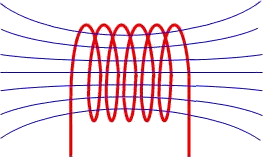
Read more at.. Benefits of Eddy Current Array Testing
Hollow Structural Sections (HSS) are steel sections in various shapes, such as round (CHS), square (SHS) and rectangular (RHS).

Read more at.. What is a Hollow Structural Section?
In many of today's industrial processes, it is essential to accurately measure the flow rate of liquids within a system, and for this purpose Flow Nozzles are applied.

Read more at.. Pipe Flow Measurement byFlow Nozzles
The primary purpose of rope access is to give workers access to hard-to-reach areas without scaffolding, wires or aerial platforms.

Read more at.. What Is Rope Access?
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has defined the term thermowell as a closed-end reentrant tube designed for insertion of a temperature-sensing element, and provided with means for a pressure-tight attachment to a vessel.

Read more at.. Temperature Measurement by Thermowell
Catalyst processing is the removal of old catalyst and loading of new catalyst into a reactor or processing unit in an oil refinery or chemical plant. This process involves several steps, which vary depending on the type of reactor and the nature of the catalyst

Read more at.. What are catalysts?
There are several methods to perform a leak test, but if water is prescribed as the fluid, use demineralised water.
Demineralised water is water completely free (or almost) of dissolved minerals as a result of one of the following processes..
- distillation
- deionization
- membrane filtration (reverse osmosis or nanofiltration)
- electrodyalisis
- or other technologies

The amount of dissolved solids in water that has followed one of these processes could be as low as 1 mg/l and is in any case always less than 10 mg/l.
The electrical conductivity is generally less than 2 mS/m and may be If water is prescribed as the fluid for a leak test, use demineralised water.even lower (<.. 0,1 mS/cm).
Pipe line freezing is a temporary method of insulating piping systems in which a freeze plug is made in the piping system so that the contents do not have to be drained. Pipe freezing is a valuable technique in the maintenance of all types of liquid storage, processing and transfer systems.
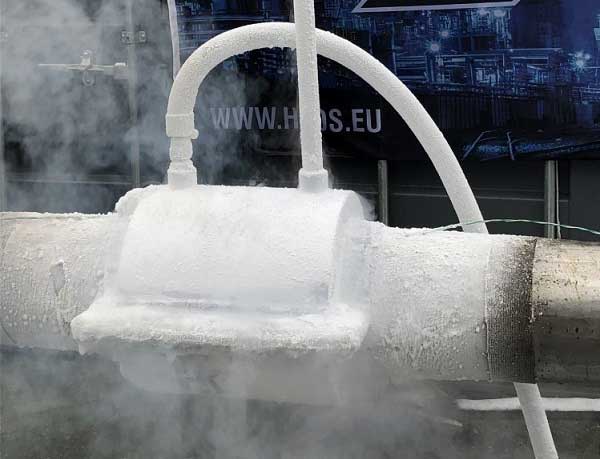

Read more at.. How pipe freezing works?
Strainers are important components of piping systems to protect equipment from potential damage due to dirt and other particles that may be carried by the process fluid.
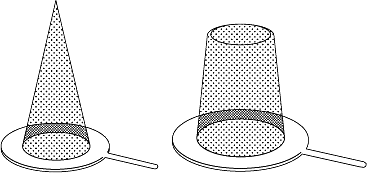
Read more at.. What is the function of a Strainer?
Victaulic is a developer and producer of mechanical pipe joining systems. Victaulic provides products for Fire Protection, Data Centers, Shipbuilding, Commercial Buildings, Mining, BioFuels, and Industrial Manufacturing.

Read more at.. Victaulic - Pipe Joining Systems
Induction Bending is a controlled means of bending pipes through the application of local heating using high frequency induced electrical power.
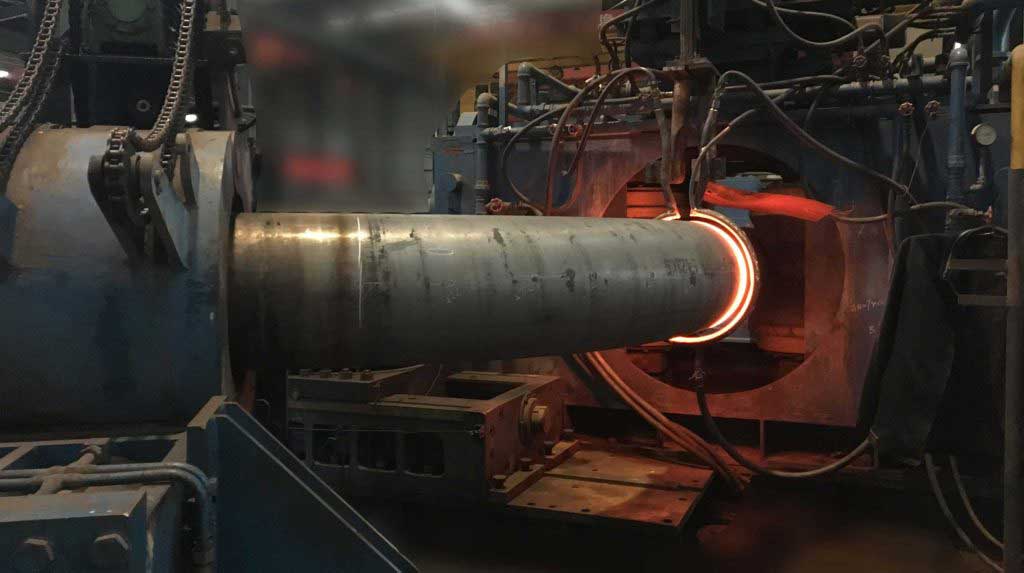

Read more at.. What is Induction Bending?
During the prefab of a flange to for example a elbow, the position of the bolt holes are of particular importance. Maybe you have ever seen the following on a drawing..
All Flange Bolt Holes Straddle the Centerlines
Read more at.. Bolt Hole Orientation
Stainless steel is a steel alloy that contains at least 10.5% chromium. The chromium reacts with oxygen in the air to form a protective layer that makes stainless steel highly resistant to corrosion and rust.

Read more at.. Does Stainless Steel rust?
Pickling and Passivation are chemical treatments applied to the surface of stainless steel to remove contaminants and assist the formation of a continuous chromium-oxide, passive film.

Read more at.. What is Pickling and Passivation?
People use the words pipe and tube interchangeably, and they think that both are the same. However, there are significant differences between pipe and tube.

Read more at.. What is the difference between Pipe and Tube?
CRA refers to corrosion-resistant alloy. The CRA cladded steel pipe is composed of a conventional carbon steel or low alloy steel pipe and a corrosion-resistant alloy layer.

Read more at.. CRA cladded pipes
FRP stands for Fiber Reinforced Plastic, and in recent years, it has been widely used in process, water and chemical industries due to their high resistance to corrosion.

Read more at.. Fiberglass Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
Weldolets (collective name - O'lets) are typically used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications where a strong and reliable connection is required. Weldolets are also used in applications where a smooth transition between the run pipe and the branch pipe is important, such as in fluid flow applications.

Read more at.. Weldolet - in details
Orifice flanges are used with orifice meters for the purpose of measuring the flow rate of either liquids or gases in the respective pipeline
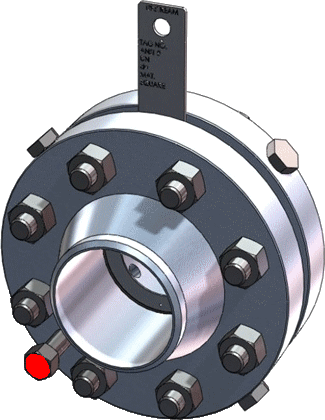
Read more at.. Orifice flanges ASME B16.36
Any steam system must be fully supported, able to expand during operation and sufficiently flexible to allow movement as a result.
Read more at.. Pipe expansion and support
Grouting is a construction technique used to fill the gaps or voids between tiles, bricks or other materials to create a strong, durable and visually appealing surface. It involves applying a dense, liquid material called grout, which is usually a mixture of cement, water and sometimes sand or other additives.
Read more at.. What is Grouting in civil construction?
A turnbuckle, also known as a stretching screw or bottle screw, is defined as “a device for adjusting the tension or length of ropes, cables, tie rods and other tensioning systems.”

Read more at.. What is a Turnbuckle?
Pipe and Tube bending methods are mainly classified into two types - hot tube bending and cold tube bending.

Read more at.. Pipe and Tube bending methods
Leaks can cost companies millions of dollars in lost energy, while increasing emissions, creating safety risks and decreasing operational reliability. With a repair clamp, a leak can be fixed without interrupting normal business operations. The methods are non-destructive, preserving equipment integrity and longevity.
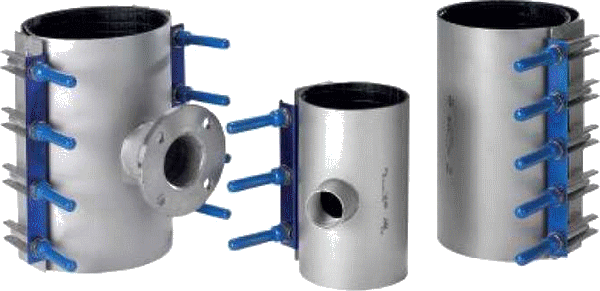
Read more at.. What are leak repair clamps?
Hot Bolting is the sequential removal, cleaning and replacement of bolts in a flanged joint, while the system is pressurized. So, based on the definition itself, you can understand that hot bolting is considered a high-risk activity.
While hot bolting is the more commonly used term, this can be misleading as the procedure Is Not Always Carried Out At a Hot Temperature. Furthermore, each of the other terms mentioned above can relate to a different process - with a distinct purpose and individual risks.

Read more at.. What is Hot Bolting?
Collars bolts are used for removable bundle heat exchangers, to holding the bundle in place, if only the channel must be removed.
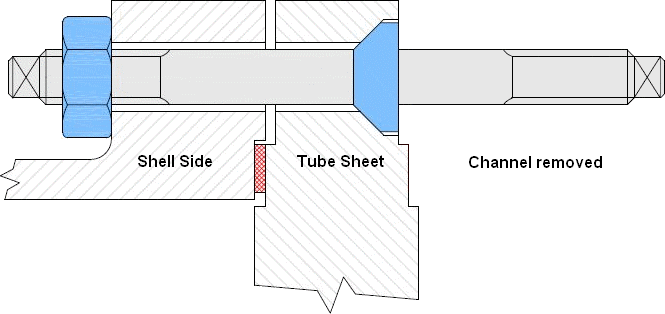
Read more at.. What are Collar Bolts and where they used?
The floating-head heat exchanger is a type of tube heat exchanger in which the tube sheet combination is independent and can move freely within the shell.
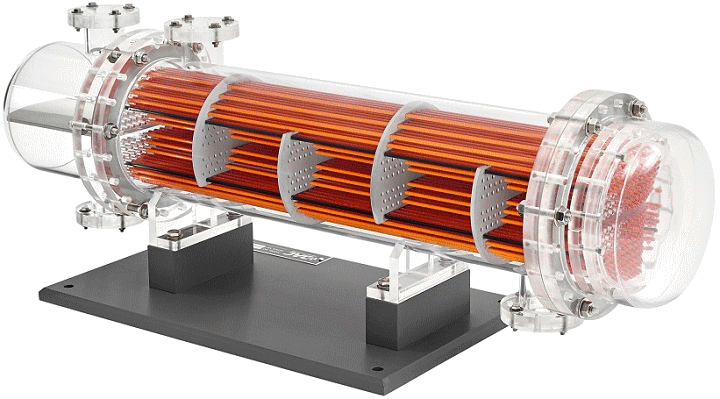
Read more at.. What Is Floating Head Exchanger?
Baron Kelvin (William Thomson) (British Scientist) once said..
"When you can measure what you are speaking about and express it in numbers, you know something about it; but when you cannot measure it, when you cannot express it in numbers, your knowledge is of a meagre and unsatisfactory kind."

In other words, you cannot manage what you cannot measure and nowhere is that more true than in the measurement of flow.
Lokring is a mechanical method for producing permanent weld equivalent pipe connections, eliminating the need for hotwork and the associated health and safety issues.

Read more at.. What is Lokring?
Pipe is held either from above by hangers or supports of various types on which it rests. Hangers are also referred to as supports.
There are a number of typical pipe supports that can be installed to support dead weight loads, and restrain the pipe for thermal and dynamic loads.
Read more at.. Typical Pipe Supports
An Orifice Plate is used to measure flow, while a Restriction Orifice is used to drop upstream pressure of a system. It is similar to an orifice plate but is thicker. While passing the fluid through thick plate energy is lost in friction and heat resulting considerable pressure drop.

Dimensions of Square Edge Orifice Plates for ASME B16.36 RF Orifice Flanges
Dimensions of Restriction Orifice Plates for ASME B16.5 RF Flanges
The removable and replaceable valve internal parts that come in contact with the flow medium are collectively termed as Valve trim. These parts include valve seat(s), disc, glands, spacers, guides, bushings, and internal springs. The valve body, bonnet, packing, et cetera that also come in contact with the flow medium are not considered valve trim.
API 600 has standardized trim materials by assigning a unique number to each set of trim materials.
The words pier and jetty are often used interchangeably, such as LNG pier or LNG jetty, both of which refer to a fixed offshore or nearshore platform that usually rises above the water on pile foundations.
In the oil and gas industry, the term Jetty refers to the "Pier" type, i.e. a platform above water used for the transshipment of oil, gas, minerals and other cargo.
Many of these Jettys are equipped with Marine Loading Arms for loading and unloading sea and inland waterway ships.

Read more at.. What are Marine Loading Arms?
The permit itself exists in many versions, and many companies use their own design. In the past, the permits were filled in by means of a paper version, nowadays this is often done electronically, where the software can help to correctly describe all the steps.

Read more at.. Hot Work Permit
- A question was put to the PM Engineer (PME) staff (one of SUPPLY HOUSE TIMES sister magazines) asking how nominal pipe size came to be. Here is the answer provided by PME Editorial Director Julius Ballanco.
- The person directly responsible for the nominal pipe size was a gentleman by the name of Robert Briggs. Briggs was the superintendent of the Pascal Iron Works in Philadelphia. In 1862, he wrote a set of pipe specifications for iron pipe, and passed them around to all of the mills in the area.
- Realize that in 1862, the United States was engaged in the Civil War. Each pipe mill made its own pipe and fittings to its own specifications. Briggs tried to standardize the sizing, which would also help the war effort. The pipe and fittings would be interchangeable between mills. This was rather novel in 1862.
- The pipe standards went on to become known as the "Briggs Standards". They eventually became the American Standards, and finally the standards used for modern day pipe.
- The current ASTM A53 Steel Pipe Standard uses basically the Briggs Standard for pipe sizes 1/2 inch through 4 inch. You will notice that after 4 inches, pipe starts to get closer to the actual dimension used to identify the pipe.
- So, you are probably asking, where did the sizes come from ?. Well, they were the sizes of the dies used in Pascal Iron Works. Briggs made everyone adjust to him. Hence, the name "nominal" pipe size came about, meaning "close to" or "somewhere in the proximity of" the actual dimension.
I found the story behind Nominal Pipe Size on..
www.supplyht.com / Supplyhouse Times
BWG -is used to determine wall thickness of pipe - in gauge and decimal parts of inch.

Read more at.. What is BWG - Birmingham Wire Gauge
Is it suitable for spiral gasket and non metallic gasket?
For what kind of application is this type?
The above questions are often asked. I try to give a correct answer.
Smooth finish flanges are more common for low pressure and/or large diameter pipelines and primarily
intended for use with solid metal or spiral wound gaskets.
Smooth finishes are usually found on machinery or flanged joints other than pipe flanges. When
working with a smooth finish, it is important to consider using a thinner gasket to lessen the
effects of creep and cold flow. It should be noted, however, that both a thinner gasket and the
smooth finish, in and of themselves, require a higher compressive force (i.e. bolt torque) to achieve
the seal.
You may have probably seen this comment..
Machining of gasket faces of flanges to a smooth finish of Ra = 3.2 - 6.3 micrometer (= 125 - 250
microinches AARH)
AARH stands for Arithmetic Average Roughness Height. It is used to measure
the roughness (rather smoothness) of surfaces. 125 AARH means 125 micro
inches will be the average height of the ups and downs of the surface.
63 AARH is specified for Ring Type Joints.
125-250 AARH (it is called smooth finish) is specified for Spiral Wound
Gaskets.
250-500 AARH (it is called stock finish) is specified for soft gaskets
such as NON Asbestos, Graphite sheets, Elastomers etc. If we use smooth finish for soft gaskets
enough "biting effect" will not occur and hence the joint may develop leak.
Sometimes AARH is referred also as Ra which
stands for Roughness Average and means the same.
Bonnet extensions are required in valves where they are subject to high or low temperatures, which can affect the integrity of the stem seals.
The extended bonnet serves to isolate the packing box from the high or low temperature zone, which helps maintain the integrity of the stem seal and the operation of the valve.

Examples of low-temperature applications and associated media include: LNG applications, liquid ethylene, oxygen, liquid hydrogen, and liquid natural gas.
Examples of high-temperature applications and associated media include: steam applications and applications with aggressive media..
In some cases, an extension may be required to place the packing box outside the insulation.
LB is the origin of the Latin word libra (weighing scale), and describes a Roman unit of mass
similar to a pound.
The full expression was librapondo, and we have invented acronyms such as..
lb = one pound, lbs = more pounds, # = Abbreviation for pound
Text below is from www.worldwidewords.org copyright © of Michael Quinion
The form lb is actually an abbreviation of the Latin word libra, which could mean a pound, itself a shortened form of the full expression, libra pondo, "pound weight". The second word of this phrase, by the way, is the origin of the English pound.
You will also know Libra as the astrological sign, the seventh sign of the zodiac. In classical
times that name was given to rather an uninspiring constellation, with no particularly bright stars
in it. It was thought to represent scales or a balance, the main sense of libra in Latin, which
is why it is often accompanied by the image of a pair of scales.
Libra for a pound is first found in English in the late fourteenth century, almost at the same
time as lb started to be used. Strictly speaking again, this was the Roman pound of 12 ounces,
not the more modern one of 16. And just to consolidate my reputation for careful description, modern
metrologists, scientists who study units of measurements, would prefer that we don't use lbs at
all; in scientific work, all units are singular.
Incidentally, another abbreviation for libra became the standard symbol for the British pound in the monetary sense. In modern times it is usually written £, an ornate form of L in which a pair of cross-strokes (often just one these days) were the way that a medieval scribe marked an abbreviation. The link between the two senses of pound, weight and money, is that in England a thousand years ago a pound in money was equivalent to the value of a pound of silver.
Grade A has lower carbon content, is a softer steel and easier to bend. Grade B has higher carbon content and tensile strength than Grade A and Grade C has higher tensile strength than Grade B.
TASTM A106 Grade A 0.25% C (max) 0.1% Si SMYS 30ksi
ASTM A106 Grade B 0.30% C (max) 0.1% Si SMYS 35ksi
ASTM A106 Grade C 0.35% C (max) 0.1% Si SMYS 40ksi
SMYS = Specified minimum yield strength for steel pipes manufactured
in accordance with a stated specification. This is a commonly used term in the oil and gas industry
for steel pipes under the jurisdiction of the US Department of Transportation.
ksi = is the abbreviated form of the unit “kilopound per square inch”
which is used to measure pressure. It is actually equal to 1000 psi (pound-force per square inch/
lbf/in^2). psi is a British unit defined as the pound-force (force exerted by gravity on a British
pound) exerted on an area of one square inch. ksi is not widely used to measure gas pressure,
but it is used primarily in materials science to measure things like tensile strength (maximum
stress an object can withstand), which is measured using a large number of “psi”.
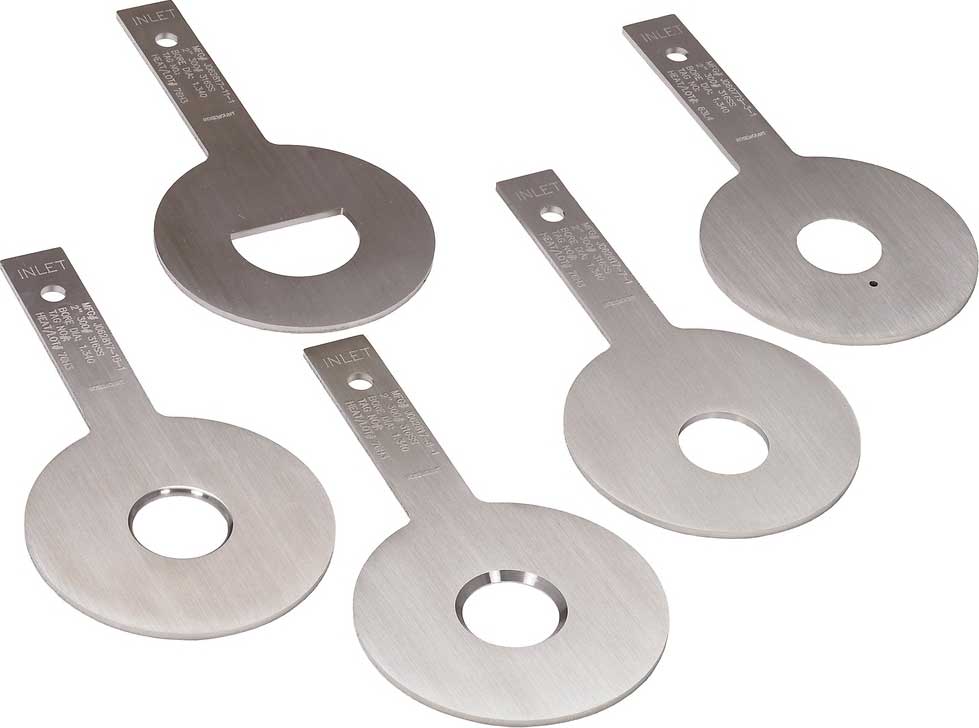
ASME B16.48 says.. spade handles may have no openings.
For spades, which can be lift up by people that's no problem, but for a spade that weighs hundreds of kilograms, a lifting ability is needed. So it is usual, that from a certain weight and size, a hole at the top of the handle is made to give a lifting possibly.
Many companies have their own rules, about the implementation of a spade handle, so there are many different types and designs.
ASME B16.48 says..The gasket seating surface finish and dimensions for raised face line blanks
shall be in accordance with ASME B16.5. A raised face may be specified at the option of the
purchaser.
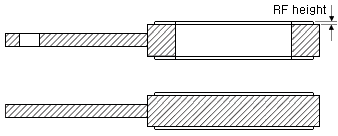
Raised Face would add machining time and complexity so the price would be higher. Call this the
Bugatti or Rolls Royce of the line blind world.
Personally, I have seen that version once or twice somewhere. The version without Raised Face
is the default and is used everywhere
Have you ever seen a Socket Weld contraction ring?.
It is a split ring that is engineered and designed to give a pre-measured 1/16" minimum gap
for socket welds. Made from a certified stainless steel, and resists corrosion from chemicals,
radioactive materials and water. Once inserted into the fitting the ring becomes a permanent part
of the joint. It will not rattle or vibrate even under extreme pressure.

Another manner is the applying of in water-soluble board. Make rings with a hole punch with outside
and inside diameter of the pipe. Insert the ring into the flange or fitting and after hydrotesting
there is no ring anymore
For both solutions, ask your customer for permission.
Read more at.. Details of Socket Weld Fittings
Heat refers to the primary melting of a metal. The heat determines the chemistry, unless the parts of the heat undergo additional treatment or refinement.
A lot or batch refers to the amount of similar items made at the same time using material of the same heat using the same manufacturing process.
I have learned, to apply a Elevation symbol and a Center-Line symbol to a isometric. Namely, the Center-Line symbol at the end of the centerline, and on that line the Elevation symbol, followed by the elevation-number.
| The sign on the left shows the centerline symbol. Tip for AutoCad users.. use the CDT font, lower case Q. | |
| The sign on the left shows the Elevation symbol. That sign, you will see on almost every isometric. |
It has become increasingly common for manufacturers to supply dual certified pipe. For example, dual certified stainless steel ASTM A312 TP304/304L and TP316/316L are widely available. Dual certification means that the material meets the maximum carbon limit of L grades, which is 0.03% C, while also meeting the higher mechanical properties of standard grade pipe.
Low carbon (L) stainless steel is used to minimize the risk of sensitization during welding. Sensitization is the formation of chromium carbides along the grain boundaries, resulting in a loss of corrosion resistance. The low carbon levels limit the amount of chromium carbides that are formed, thereby limiting the depletion of chromium along the grain boundaries. Therefore, grade 304L offers better corrosion resistance, especially when welding.
The photo shows an incorrectly tightened flange, because two bolts are too short, causing the nuts not to sit completely on the bolts.

This means that the joint may not be as strong as it should be. Flanges are designed so that the entire nut-bolt combination holds the forces on the flange. If the nut is only partially screwed onto the bolt, the connection may not be strong enough.
You knew that...?
At the smallest sizes, the amount of wall lost during threading actually equals approximately 55% of the original pipe wall.

SHELL MESC stipulates a pressure equalizing hole of at least 3 mm in the ball. It states that the Cryogenicball valve must have an automatic way to relieve overpressure
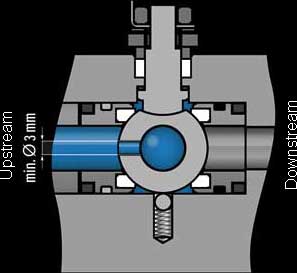
Read more at.. What are Cryogenic Valves?
On February 7, 2009, one worker was killed and 15 people were injured in an explosion at a construction site in Shanghai's Yangshan Deep Water Port.

The explosion was caused by a sudden flange rupture while workers were performing pneumatic tests on a 36-inch pipe.
Read more at.. Potential Dangers associated with Pneumatic Testing
Hot Taps or Hot Tapping is the ability to safely tie into a pressurized system, by drilling or cutting, while it is on stream and under pressure.
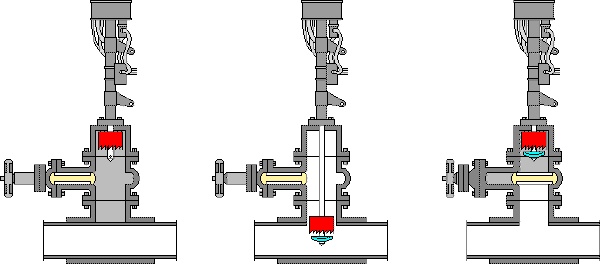
Read more at.. Introduction to Hot Tapping and Line Stopping
On my website, in the Documents menu you will find symbols applied
to Isometrics, Piping and Instrumentaton Diagrams (PIDs) etc. All symbols are taken from drawings
that I have handled myself, but almost every client and engineering company uses their own symbols,
and some, with the same description can be seen in multiple versions.
A standard for all these symbols, would perhaps be an option.
On my website, you can watch videos made by others. Sometimes it happens that the link gives an error message because the owner of the video has made changes. All links to the relevant videos are regularly checked by me

But it can still happen that an error occurs. If that is the case, I would be grateful if you
let me know, through this Link
Thank you
A lot of pictures on this website are photographed by myself. But there are also a lot of pictures I got through people I know and the World Wide Web. Pictures of others I basically give a caption where I found the picture with the corresponding website URL.
There are two reference points for measuring pressure. When the reference point is standard atmospheric pressure, the measured pressure is called gauge pressure and is written psig. When the reference point is a perfect vacuum, the measured pressure is called absolute pressure and is written with psia.

- Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level is 14.696 psia = 0 psia
- Perfect vacuum = 0 psia = -14.696 psia
- Absolute pressure (psia) = gauge pressure + 14.7 psia
The differences between a HEA, HEB and a HEM beam is generally in the thickness dimensions of the three planes. But there are also substantial differences in the width and height dimensions. (In the past I once made quite a HEA mistake with the W - H dimensions, to assume something, while the reality was not the same.)
The link below will take you to the dimensions of the mentioned beams...
For pipelines equipped with copper steam tracing tubes and insulated for this reason, it must be ensured that threaded fittings used to mount the tubes are definitely not placed under the insulation.
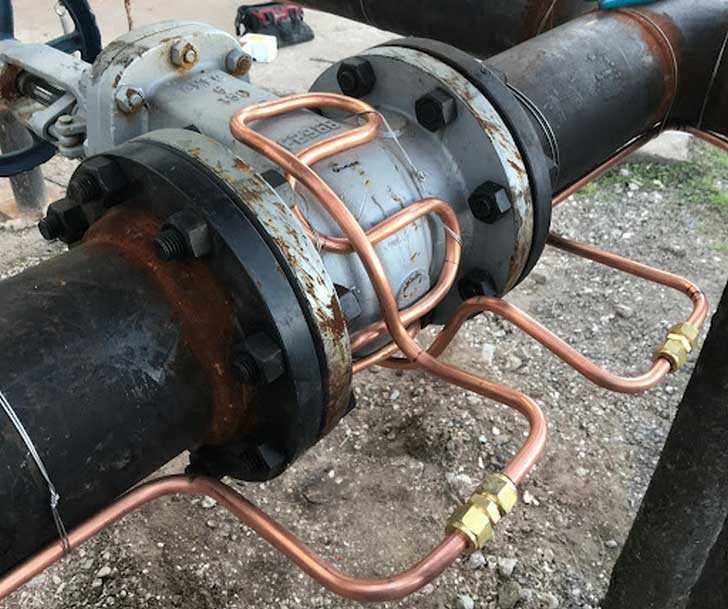

The link below may tell you why...
Heat Tracing of Piping Systems
It is Steel that has been completely deoxidized by the addition of an agent such as silicon or alumimium, before casting, so that there is practically no evolution of gas during solidification. Killed steels are characterized by a high degree of chemical homogeneity and ;freedom from porosity.
We say the steel is "killed" because it will quietly solidify in the mould, with no gas bubbling out. As a result, killed steel is dense in structure, uniform in composition, and not so segregative as other types of steels.
Background
During the steel making process, oxygen may become dissolved in the liquid metal. During solidification,
the dissolved oxygen can combine with carbon to form carbon monoxide bubbles. The carbon is added
to the steel as an alloying element.
The carbon monoxide bubbles are often trapped in the casting and can act as initiation points for
failure.
How Killed Steels are Produced and Their Advantages
Formation of the carbon monoxide bubbles can be eliminated through the addition of deoxidising
agents such as aluminium, ferrosilicon and manganese. In the case of aluminium, the dissolved
oxygen reacts with it to form aluminium oxide (Alumina, Al2O3). The formation of alumina not only
prevents the formation of bubbles or porosity, but the tiny particles or inclusions also pin grain
boundaries during heat treatment processes, preventing grain growth.
Completely deoxidised steel are known as "killed steels".
They have a more uniform analysis and are relatively free from ageing.
For a given carbon and manganese content, killed steels are usually harder then rimmed steels.
The disadvantage of using killed steels is they often display deep pipe shrinkage.
Steels that are typically killed and are generally killed include..
- Steels with carbon contents greater then 0.25%
- All forging grades of steel
- Structural steels with carbon content between 0.15 to 0.25%
- Some special steel in the lower carbon ranges
Code requirements for minimum spacing between welds are not or hardly specified.
The minimum spacing between pipe welds is usually specified in the fabrication or installation specifications and is not a code requirement. If a weld must be made that is not shown on the isometric drawing, it must be approved by the piping designer.
Pipeline specifications from engineering companies and multinationals such as Shell, Exxon, BP, etc. usually specify what the minimum spacing should be.
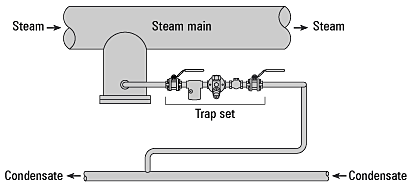
The duty of a steam trap is to discharge condensate, air and other incondensable gases from a steam system while not permitting the escape of live steam.

`Read more on.. What are Steam Traps?
Reduced bore valves have a smaller ball size than full bore valves and consequently the body (casting or forging) is smaller for reduced bore ball valves. This results in lower construction costs and lower weight. The smaller ball size also results in lower operating torque and lower cost of the actuator for the valve. The pressure drop across a reduced bore valve will be marginally higher than for full bore valves.

Where pressure drop becomes very critical, full bore valves are supplied instead of reduced bore valves. Full bore valves are also supplied in special applications such as in pipelines to facilitate pigging and for hot tapping applications .
A deadman handle is a spring return valve designed for applications where fluids need to be drained or sampled.

The valve can be opened by the operator, but once the operator releases the handle, it springs back to the closed position, automatically closing the valve. A deadman handle provides a safe, economical, and reliable way to automatically close manual valves.
Often I hear individuals talking about ANSI flanges. Probably because a particular customer's system has never upgraded its own standards, or because an older plant has ANSI described on the flanges. For years ANSI has not been the American standard for flanges e.g. but has become an ASME standard.

Do you see the ANSI marking on the flange?
The link below can tell you more about that...
ANSI B16 or ASME B16?
For the correct length of a stud bolt, you can use the following as a rule of thumb.
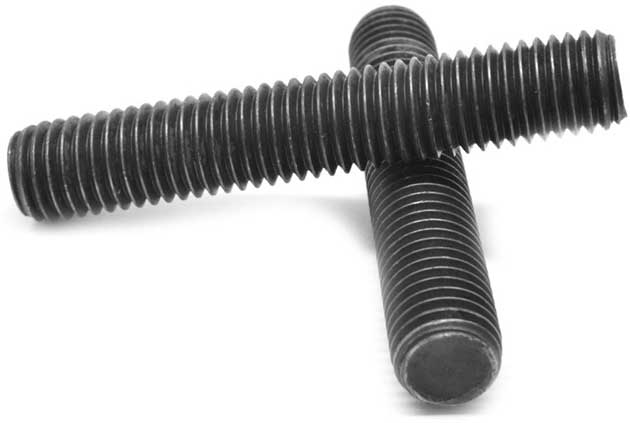

The free threads of the bolt above the top of the nut is equals to 1/3 times the bolt diameter.
When a gate valve is opened, the area of the opening does not increase linearly with stem movement. That is, the flow velocity across the valve does not increase linearly with stem movement.
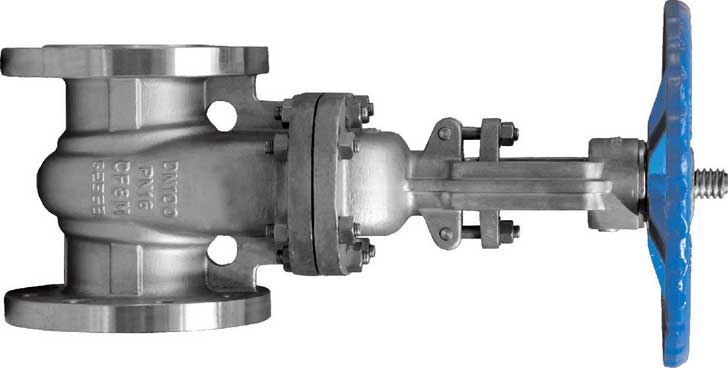
When a gate valve is opened, fluid flows over the valve at high velocity, causing erosion on the disc and seats, ultimately causing leakage across the seats. In the partially open position, the valve disc is also sensitive to vibration. Therefore, gate valves are not considered suitable for regulating or throttling flow.
Parallel gate valves consist of two discs with a spring mounted between the two discs. The discs are held lightly against the body seats by the springs to provide the initial sealing force. The springs do not provide the seating force.

Read more at.. Parallel slide gate valve
Drip Legs are vertical pipe pockets along the main steam line where condensate is collected for drainage from the system.

`Read more on.. What are Drip Legs in Steam Piping?
The link below shows you how to do that....
The solid wedge gate valve is the most commonly used type of gate valve. The wedge is a one-piece construction that is machined to fit the body seat to provide a tight seal.

The disadvantage of a solid wedge is that it is prone to seizing when there is slight deformation in the valve body due to thermal expansion or bending loads. The flexible wedge gate valve overcomes this limitation. In a flexible wedge design, the wedge is provided with an annular groove that allows the wedge to flex in the body seat. The flexible wedge can accommodate deformation in the valve body.

The height of a nut for a Stud Bolt ASME B16.5 and ASME 16.47 is the same as the diameter of the thread rod.
In Pressure Classes 150 and 300, the height of raised face flange is approximately 1.6 mm (1/16 inch).

In Pressure Classes 400, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500, the height of raised face is approximately 6.4 mm (1/4 inch).
NPS stands for Nominal Pipe Size, and indicates the standard pipe size followed by the size designation without an inch symbol. For example, NPS 8 refers to a pipe with a nominal pipe size of 8 inches. For sizes 14" and larger, the NPS is equal to the outside diameter in inches..
DN stands for Diameter Nominal and is used in the metric system of units. DN indicates the standard pipe size followed by the size designation without a millimeter symbol. For example, DN 100 refers to a pipe with a nominal diameter of 100 mm. The equivalent designation is NPS 4.
Related Post(s)

Answers to questions regarding industrial piping related issues and topics...
