Stub-in and Stub-on connections in Piping systems
Stub-in and Stub-on connections are two essential techniques used in the pipeline industry to safely connect pipes together. In the world of piping, efficient and reliable joints are paramount for the safe and smooth transport of fluids. These methods ensure structural integrity, prevent leaks and facilitate maintenance.
What are Stub-in connections?
Stub-in connections, also known as branch or lateral connections, involve connecting a smaller pipe or branch to a larger main pipe. This technique is widely used when a diversion or branch from the main pipe is needed for various purposes, such as distribution, control or instrumentation.
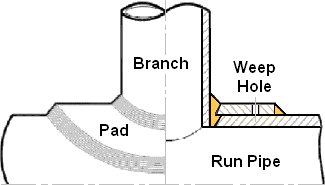
Key features of Stub-in connections:
- Welding: Stub-in connections are made by welding, which ensures a secure and leak-free connection.
- Reduced stress concentration: Proper design and application of Stub-in connections can help distribute stress and minimise concentration points.
- Diverse applications: These joints find applications in petrochemicals, water treatment and HVAC systems.
Advantages of Stub-in connections:
- Space saving: Stub-in connections take up less space than some alternatives.
- Smooth flow transition: Well-designed Stub-in connections offer a smooth transition of fluid flow, minimising pressure losses.
Important considerations for Stub-in connections
Several factors must be taken into account when using Stub-in connections to ensure optimum performance and long life.
- Material compatibility: The material of the Stub-in pipe should be compatible with the material of the run pipe.
- Welding techniques: Choosing the right welding technique is crucial for a strong and durable connection. Factors such as pipe material, thickness and welding expertise come into play.
- Stress analysis: Performing a stress analysis helps determine potential stress points and guides joint design to reduce stress concentration.
- Correct alignment: Accurate alignment during installation is essential to avoid problems with misalignment in the future.
- Maintenance access: When installing Stub-in connections, consider accessibility for maintenance and possible future modifications.
Exploring Stub-on connections
Stub-on connections, also called saddle connections or saddle taps, consist of attaching a saddle-like fitting to the main pipe to make a branch connection. This technique is often used for smaller pipes or temporary connections.

Key features of Stub-on connections:
- Easy installation: Stub-on connections are relatively easier to install compared to some other methods, making them suitable for quick installations.
- Versatile applications: These connections are often used in irrigation systems, temporary test setups and situations where permanent connections are not needed.
Advantages of Stub-on connections:
- Cost-effectiveness: Stub-on connections are cost-effective thanks to the simple installation process and lower material requirements.
- Temporary solutions: They can serve as temporary solutions or test points without the need for extensive modifications to the main pipeline.
Important considerations for Stub-on connections
Although Stub-on connections offer simplicity, certain considerations must be taken into account for reliable performance.
- Pressure limitations: Stub-on connections may have pressure limitations compared to more robust connection methods, making them suitable for specific scenarios.
- Leakage potential: Improper installation or poor-quality saddle connections can lead to leakage, highlighting the importance of quality materials and workmanship.
- Service life: Stub-on connections may not have the same durability as more permanent solutions, so their service life should be evaluated based on their intended use.
Differences between Stub-in and Stub-on connections
Complexity of installation:
Stub-in connections usually require more precise welding and alignment, making them more complex to install than Stub-on connections.
Stub-in connections are usually stronger and more durable than Stub-on connections due to their welded joints and careful alignment.
Stub-on connections are easier and faster to install thanks to their saddle-shaped design.
Applications:
Stub-in connections are often used for permanent branch connections, while Stub-on connections are often used for temporary or test purposes.
Durability and longevity: Stub-in connections, when properly installed, generally offer greater durability and longer service life than Stub-on connections.
Pressure handling: Stub-in connections are better suited to high-pressure applications. Stub-on connections are ideal for low- to medium-pressure scenarios.
Conclusion
In terms of piping systems, the choice between Stub-in and Stub-on connections depends on factors such as the intended application, pressure requirements, complexity of installation and long-term durability. Stub-in connections offer robustness and structural integrity for permanent installations, while Stub-on connections offer simplicity and versatility for temporary or low-pressure scenarios.
Related Post(s)

Hot Taps or Hot Tapping is the ability to safely tie into a pressurized system, by drilling or cutting, while it is on stream and under pressure...